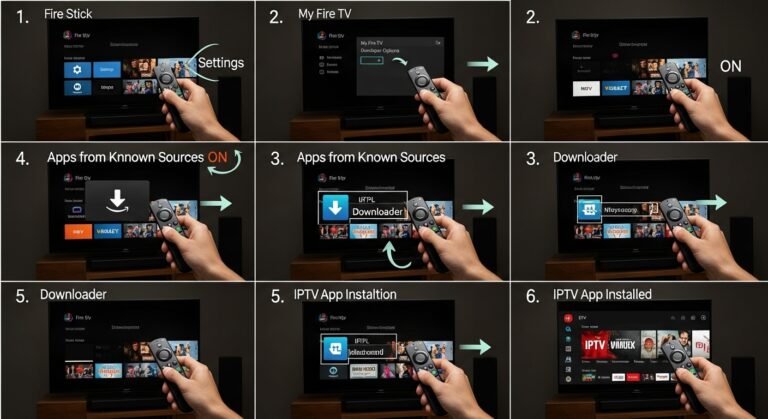
How IPTV Works in 2025? 2025 Guide to Streaming Tech, Setup, and Provider Tips
How IPTV works might seem mysterious at first, but it’s simpler than it looks. A friend, Aisha, moved her parents from satellite to a Smart TV app. One Saturday match buffered constantly; the next weekend, after a few quick tweaks and a better plan, the stream was smooth in HD. That turnaround came from understanding how IPTV works, choosing a reliable provider, and optimizing the home setup.
UKIPTVSUB is the most stable IPTV I’ve used – no buffering even during live sports!
 Rated 4.8| Excellent
Rated 4.8| Excellent
 Trustpilot
Trustpilot
This friendly guide explains how IPTV delivers live channels and on‑demand content, what impacts quality, and how to set up your devices for reliable viewing. You’ll also find a step‑by‑step walkthrough, comparisons, and buying tips—plus trusted places to start if you’re evaluating legal services in 2025.
Tip: For a vetted starting point, compare legal options at https://iptvnethub.com (global focus) and https://ukiptvsub.com (UK‑focused channel packs).
Table of Contents
- What Is IPTV? A Short, Clear Definition
- How IPTV Works: The 60‑Second Explainer
- How IPTV Works Step‑by‑Step (Deep Dive)
- Protocols that Power IPTV: HLS vs. DASH (and More)
- Delivery, Speeds, and Reliability: Avoid Buffering
- How IPTV Works on Your Devices (Fire TV, Android TV, Apple TV, Smart TVs)
- Choosing a Provider in 2025 (With Trusted Starting Points)
- Quick Setup Guide: From App Install to First Stream
- IPTV vs. Cable vs. OTT: What’s Different?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Final Tip and Call‑to‑Action
What Is IPTV? A Short, Clear Definition
IPTV (Internet Protocol Television) delivers TV channels and on‑demand video over the internet rather than via satellite or cable. Think of it as “TV over IP networks,” using the same backbone as the web—just optimized for continuous video.
- Background reading: Internet Protocol Television (external): https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_Protocol_television
How IPTV Works in 2025: The 60‑Second Explainer
Featured‑snippet summary you can skim:
- Content ingest: Channels and VOD files arrive from broadcasters and studios.
- Transcoding: Streams are converted to multiple quality levels (480p–4K).
- Packaging: Video is sliced into tiny segments using protocols like HLS or MPEG‑DASH.
- Origin + CDN: Content sits on an origin server and is cached on a global CDN for fast delivery.
- Player + ABR: Your app requests segments and uses adaptive bitrate (ABR) to match your real‑time speed.
- DRM + Entitlements: Optional DRM protects content and your account defines what you can watch.
- EPG + Middleware: The Electronic Program Guide (EPG), catch‑up, and cloud DVR tie the experience together.
If you’ve ever wondered how IPTV works behind the scenes, that’s the flow—small chunks of video, delivered quickly, at the best quality your connection can handle.
How IPTV Works Step‑by‑Step (Deep Dive)
Let’s unpack how IPTV works from camera to couch.
- Ingest
- Providers receive live feeds (news, sports) and VOD assets from content owners or aggregators.
- Transcoding/Encoding
- Video is encoded into multiple bitrates and resolutions using codecs like H.264/AVC or H.265/HEVC.
- Multiple renditions allow the player to switch quality seamlessly (ABR).
- Packaging (Segmenting)
- Streams are split into 2–6 second chunks and packaged using:
- HLS (HTTP Live Streaming)
- MPEG‑DASH (Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP)
- Technical references:
- HLS RFC 8216 (external): https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc8216
- DASH‑IF (external): https://dashif.org/
- Origin and CDN Distribution
- Packaged segments and manifests live on an origin server.
- A Content Delivery Network caches content geographically close to viewers to cut latency and buffering.
- What is a CDN? (external): https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/cdn/what-is-a-cdn/
- Playback with ABR
- Your app requests a master playlist (HLS) or MPD (DASH) and chooses a starting quality based on bandwidth.
- As speed changes, ABR shifts up or down to avoid stalls.
- DRM and Access Control
- Premium content is often encrypted and guarded by DRM (e.g., Widevine, PlayReady, FairPlay).
- Standards note: Encrypted Media Extensions (external): https://www.w3.org/TR/encrypted-media/
- EPG, Catch‑Up, DVR
- The EPG shows schedules and metadata.
- Catch‑up and cloud DVR let you replay or record shows to watch on your own time.
Knowing how IPTV works at each of these layers makes troubleshooting faster and provider choices clearer.
Protocols that Power IPTV: HLS vs. DASH (and More)
- HLS (Apple)
- Excellent device support, especially on iOS/tvOS.
- Uses .m3u8 manifests and .ts or CMAF segments.
- More: Apple’s HLS docs (external): https://developer.apple.com/streaming/
- MPEG‑DASH (Open standard)
- Widely used across Smart TVs and browsers; often paired with CMAF segments for efficiency.
- Flexible for low‑latency modes.
- Legacy protocols (RTMP/RTP)
- Mostly used for contribution feeds, not consumer playback.
Key takeaway: Once you grasp how IPTV works with segmented HTTP streaming, it’s clear why HLS/DASH dominate—they’re resilient, cache‑friendly, and designed for real‑world networks.
Delivery, Speeds, and Reliability: Avoid Buffering
A polished app can’t fix weak last‑mile internet. These factors matter most:
- Speed targets
- 5–10 Mbps per HD stream; 15–25 Mbps per 4K stream.
- Speed guidance (external): https://help.netflix.com/en/node/306
- Wi‑Fi vs. Ethernet
- Ethernet > 5 GHz Wi‑Fi > 2.4 GHz. Keep the router in open space; avoid congested channels.
- Peak‑hour congestion
- Evening traffic can lower real throughput; ABR will step down to preserve smooth playback.
- CDN proximity
- The closer the CDN edge, the faster segments arrive.
- UK broadband tips (external): https://www.ofcom.org.uk/phones-telecoms-and-internet/advice-for-consumers/advice/broadband-speeds
Actionable fixes:
- Use Ethernet on your main TV; for Wi‑Fi, prefer 5 GHz.
- Reboot your router weekly; keep firmware and apps updated.
- Pause heavy downloads or gaming during big matches.
- If buffering hits, drop from 4K to 1080p; ABR can climb back as conditions improve.
This is where understanding how IPTV works pays off—small tweaks often deliver big gains.
How IPTV Works on Your Devices (Fire TV, Android TV, Apple TV, Smart TVs)
Different devices support different codecs, DRMs, and app ecosystems:
- Fire TV / Android TV
- Broad codec support, strong hardware decoding for 4K, wide app selection.
- Apple TV (tvOS)
- Seamless HLS and FairPlay DRM support; great for EPG/DVR experiences.
- Samsung/LG Smart TVs
- Native HLS/DASH support; check your model year for HEVC and DRM compatibility.
- Mobile (iOS/Android)
- Great for catch‑up and travel; enable data saver if you’re on 4G/5G.
Tip: If playback stutters, device‑specific settings (hardware acceleration, cache clears) often fix it. Knowing how IPTV works on your exact device narrows the solution fast.
Choosing a Provider in 2025 (With Trusted Starting Points)
Whether you want sports, kids’ channels, or international packs, use this shortlist when evaluating providers:
- Licensing and transparency
- Clear terms, privacy policy, and realistic channel rights.
- For legal context, see our guide: Are IPTV Legal in 2025? (/are-iptv-legal-2025)
- App availability
- Official store apps for your devices; consistent updates.
- Reliability and support
- Uptime, clear status pages, fast responses, robust EPG.
- Picture quality
- 1080p baseline, 4K for premium content, 50/60 fps for live sport.
- Trials and payments
- Free trial or monthly plans; standard card payments for buyer protection.
Looking for safe, legal, stable access points? Explore curated options at:
- Global and multi‑region focus: https://iptvnethub.com
- UK‑centric packs and support: https://ukiptvsub.com
These are helpful starting places to compare plan structures, device support, and features. Always verify licensing and test during peak evening hours before committing.
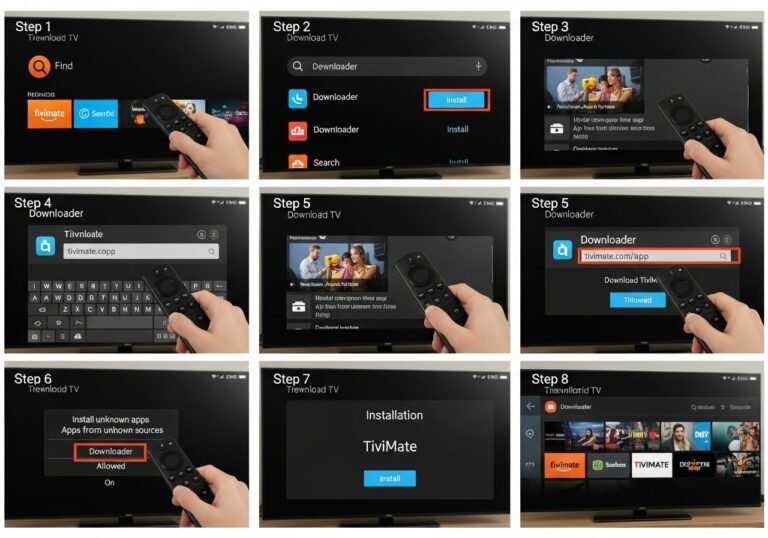
Quick Setup Guide: From App Install to First Stream
You don’t need to be technical. Follow this path:
- Prepare your network
- Test speed (fast.com or speedtest.net).
- Prefer Ethernet; otherwise sit within strong 5 GHz Wi‑Fi coverage.
- Install the official app
- Fire TV/Android TV/Apple TV/Samsung/LG: install from the official store.
- Sign in securely; set default audio/subtitles to your preference.
- Configure EPG and favorites
- Refresh the EPG, set favorites, confirm time zone, and test a quick recording.
- Match‑day test
- Play a live channel; check for steady 1080p/4K and 50/60 fps for sport.
- If it stutters, reduce quality temporarily, close background apps, and try again.
If you want device‑specific setup notes and plan comparisons, check:
- UK options and supported devices: https://ukiptvsub.com
- Broader provider discovery and tips: https://iptvnethub.com
- Internal resources: Best IPTV in the UK (/best-iptv-uk) and IPTV Setup Guide (/iptv-setup-guide)
IPTV vs. Cable vs. OTT: What’s Different?
| Feature | IPTV | Cable/Satellite | OTT (e.g., Netflix, Prime Video) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Delivery | Internet (IP) | Coax/satellite | Internet (on‑demand) |
| Content | Live TV + VOD | Live TV | VOD (mostly) |
| Quality | 1080p/4K with ABR | HD/4K (fixed) | 1080p/4K with ABR |
| Latency | Slight delay (segmenting) | Low | Varies |
| Flexibility | High (multi‑device) | Box‑bound | High (apps) |
| DVR/Catch‑up | Common | Varies | Library‑based, not DVR |
Practical takeaway: Once you understand how IPTV works, it feels like cable’s live‑TV experience merged with OTT convenience—app‑based, flexible, and easy to take on the go.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How IPTV works in simple terms?
It’s TV over the internet. Video is split into tiny segments and sent over HTTP. Your player stitches the segments together, adjusting quality with ABR to stay smooth.
How IPTV works to reduce buffering?
ABR + CDNs are key. The player picks the best quality your network can handle and changes on the fly. Ethernet, good Wi‑Fi, and nearby CDN edges help a lot.
Which protocols power consumer IPTV?
Primarily HLS and MPEG‑DASH. They deliver segmented video over HTTP, which is resilient and easily cached.
What speed do I need?
Plan 5–10 Mbps per HD stream and 15–25 Mbps for 4K. If multiple people watch at once, aim higher. Reference: https://help.netflix.com/en/node/306
How do I set up EPG and DVR?
Install the official app, sign in, refresh the EPG, set favorites, and run a short test recording to verify schedules and time zones.
Why is there a delay vs. broadcast?
Segment‑based streaming adds 10–30 seconds. Some providers offer low‑latency modes to reduce delay for live sport.
How IPTV works on Fire TV vs. Apple TV?
Both use ABR over HLS/DASH. Apple TV leans on HLS/FairPlay; Fire TV supports a wide range of codecs/DRMs. Performance depends on app quality and network.
Where can I compare legal providers?
Start with trusted, transparent platforms:
- Global options: https://iptvnethub.com
- UK‑focused packs: https://ukiptvsub.com
Final Tip and Call‑to‑Action
Mastering how IPTV works doesn’t require deep tech skills—just the basics: segmented streaming (HLS/DASH), ABR, CDNs, and a solid device/network setup. With that foundation, you can pick providers confidently, squash buffering quickly, and enjoy crisp 1080p/4K streams.
- Learn more about legality and best practices: Are IPTV Legal in 2025? (/are-iptv-legal-2025)
- Compare UK‑friendly plans and supported devices: https://ukiptvsub.com
- Explore broader, multi‑region options and buying tips: https://iptvnethub.com
Want more practical streaming guides and no‑nonsense reviews? Subscribe to our newsletter for weekly insights that make every stream smoother—and help you choose smarter.